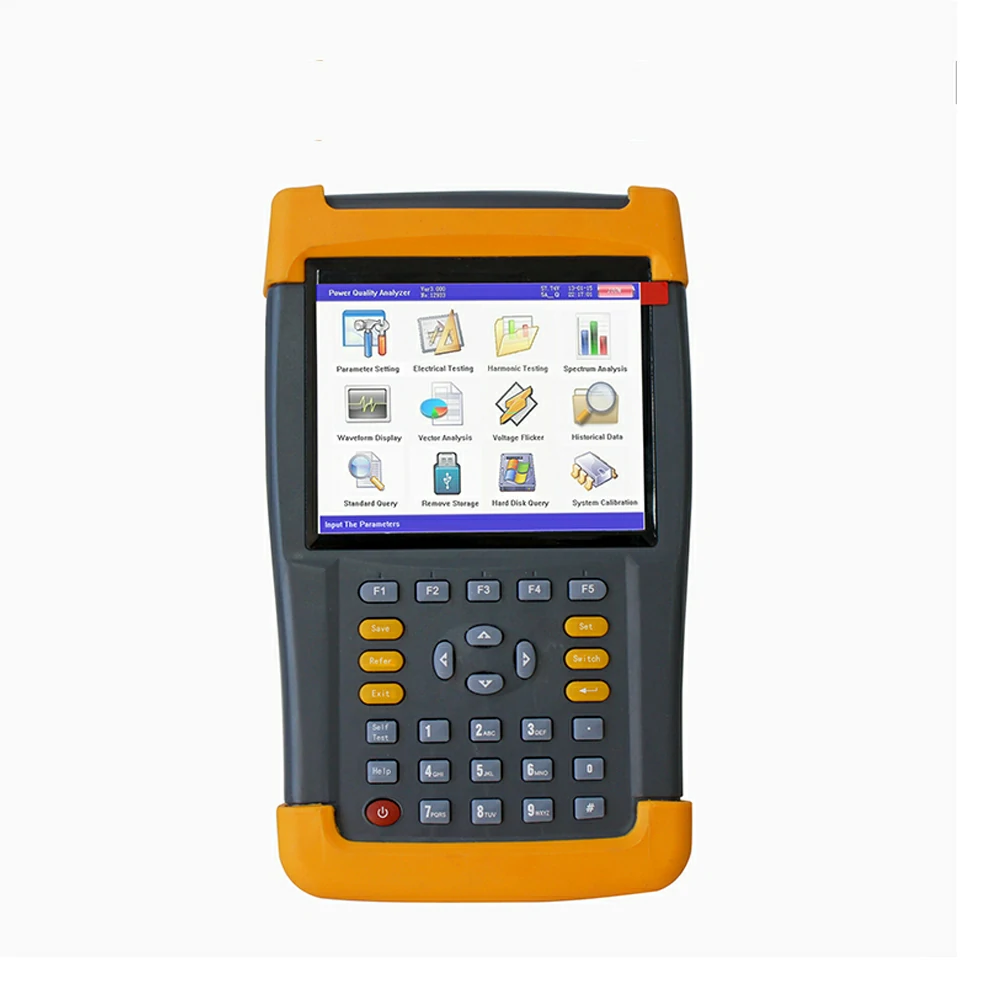
Electrical test meters, such as multimeters or insulation resistance testers, are primarily designed to measure electrical parameters and assess the condition of electrical components, systems, and insulation. While these meters are not typically used to directly handle or analyze oil samples with additives or modifiers, the presence of additives or modifiers in oil-filled equipment can indirectly impact electrical testing in several ways:
- Dielectric Properties: Additives or modifiers in oil can alter the dielectric properties, such as permittivity, dissipation factor, and breakdown voltage, of the oil-insulated components. Electrical test meters may detect variations in these properties during insulation resistance testing or dielectric strength testing, providing insights into the condition of the insulation system.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Insulation resistance testers are used to assess the integrity of electrical insulation by measuring the resistance between conductive surfaces and ground. Additives or modifiers in oil can affect the insulation resistance readings by influencing the conductivity or resistivity of the oil-insulated components. Electrical test meters may detect deviations from expected resistance values, indicating potential issues with insulation integrity.
- Dielectric Strength Testing: Dielectric strength testers evaluate the ability of insulation materials, including oil, to withstand electrical stress without breakdown. Additives or modifiers in oil may affect the breakdown voltage or withstand voltage of the insulation, impacting the results obtained during dielectric strength testing. electrical test meter Electrical test meters may detect anomalies in voltage levels or breakdown behavior, indicating variations in oil quality or composition.
- Temperature Compensation: Some electrical test meters incorporate temperature compensation features to account for variations in ambient temperature during testing. Additives or modifiers in oil can influence the thermal conductivity or heat dissipation properties of the oil-insulated components, affecting temperature-dependent measurements obtained with electrical test meters.
- Calibration Considerations: Electrical test meters used for oil-filled equipment testing may require calibration adjustments or corrections to account for the presence of additives or modifiers in the oil. Calibration procedures ensure the accuracy and reliability of test meter measurements and help mitigate the impact of oil-related factors on testing results.
Overall, while electrical test meters are not specifically designed to handle oil samples with additives or modifiers, they can indirectly assess the condition of oil-insulated components by measuring electrical parameters and detecting variations in insulation properties. Proper interpretation of test meter readings, consideration of oil-related factors, and adherence to relevant standards and procedures are essential for accurate and reliable electrical testing of oil-filled equipment.